KIDNEY STONE DISEASE DESCRIPTION CAUSES SYMPTOMS
Kidney stones (also known as nephrolithiasis or nephrolithiasis) are solid deposits of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys. The USA Best Doctors provide the best treatment in medical field. Lifestyle and diet, overweight, certain diseases, and certain supplements and medications are some of the many causes of kidney stones.
Kidney stones affect any part of the urinary tract - from the kidneys to
the bladder. Often rocks are formed when the urine becomes concentrated, which
leads to crystallization and sticking of stones. The passage of kidney stones
is quite painful, but the stones do not cause irreversible damage if detected
in time. Depending on your situation, you may only need to take painkillers and
drink plenty of water to get rid of kidney stones. In other cases, surgery is
required when stones get stuck in the urinary tract, are associated with a
urinary tract infection, or cause complications. In addition, the doctor
recommends preventive treatment to reduce the risk of recurrence of kidney stones
if the patient has an increased risk of their formation.
Symptoms of kidney stones:
The stones do not cause symptoms until they begin to move inside the
kidneys or enter the ureter. If the stone is stuck in the ureter, it blocks the
outflow of urine and causes swelling of the kidneys and spasm of the ureter.
This condition is excruciating for the patient and requires urgent care.
Main symptoms:
- severe sharp pain in the
side and back, below the ribs;
- pain in the lower abdomen
and groin;
- wavy nature of pain and
fluctuations in intensity;
- burning when urinating,
pain;
- pink, red or brown urine;
- sharp, unpleasant during
urination;
- constant urge to urinate (as
in cystitis);
- nausea, vomiting;
- Fever chills.
When to see a doctor?
Contact your doctor immediately if you have any of the following
symptoms:
- the pain is so severe that
you cannot sit still or find a comfortable position;
- pain accompanied by nausea
and vomiting;
- fever and pain chills;
- Blood in the urine and
difficulty urinating.
Causes of stone formation
Kidney stones often do not have a specific cause, although several factors increase the risk. Rocks are formed when urine contains large amounts of crystal-forming substances such as calcium, oxalates, and uric acid. The best doctors in USA provide more facilities in medical field. At the same time, it does not contain substances that prevent the adhesion of crystals, which creates an ideal environment for the formation of stones.
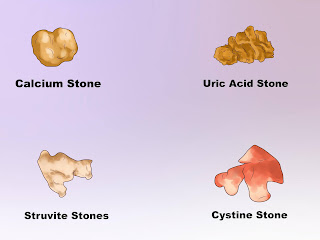
Types of stones
Knowing the types of kidney stones helps determine their cause and gives tips on reducing the risk of more stones.
Types of kidney stones:
- Calcium stones. Most stones
are calcium stones, usually in the form of calcium oxalate. Oxalate is a
substance that is produced daily by the liver or ingested with food. Some
fruits and vegetables, as well as nuts and chocolate, contain large
amounts of oxalates. Dietary factors, high doses of vitamin D, bowel
bypass surgery, and metabolic disorders increase the concentration of
calcium or oxalates in the urine. Calcium stones also sometimes consist of
calcium phosphate. This type of stone is more common in metabolic
disorders such as renal tubular acidosis.
- Struvite stones. They are
formed in response to a urinary tract infection. These stones multiply and
become large.
- Uric acid stones. They
included patients who lose too much fluid due to chronic diarrhea or
malabsorption, those who follow a diet high in protein, and people with
diabetes or metabolic syndrome. Certain genetic factors also increase the
risk of uric acid stones.
- Cystine stones. These stones
form in patients with an inherited disease called cystinuria, in which the
kidneys excrete too many specific amino acids.
Risk factors for stone formation
Factors that increase the risk of developing kidney stones:
- Family or personal history.
If someone in your family has had kidney stones, you are more likely to
have them.
- Dehydration. Insufficient
water intake increases the risk of stone formation.
- Certain diets. Adherence to
a diet high in protein, sodium (salt), and sugar increase the risk of
certain types of kidney stones. This is especially true for a diet high in
sodium. Too much salt in the diet increases the amount of calcium that the
kidneys need to filter.
- Digestive diseases and
surgical interventions. Gastric bypass surgery, inflammatory bowel
disease, or chronic diarrhea cause changes in the digestive process that
affect the absorption of calcium and water, increasing the amount of
stone-forming substances in the urine.
- Other diseases such as renal
tubular acidosis, cystinuria, hyperparathyroidism, and recurrent urinary
tract infections.
- Dietary supplements and
medications such as vitamin C, laxatives (when used excessively),
calcium-based antacids, and certain medications used to treat migraines or
depression.



Comments
Post a Comment